Summary
This video provides a comprehensive walkthrough on how to create, manage, and configure permissions for a Project using JuliaHub. Deep begins by guiding users through the initial steps of creating a new project, including naming the project, adding descriptions and tags, and selecting a default application environment such as the Julia IDE. The tutorial emphasizes the importance of choosing the appropriate workflow—either exclusive editing or collaborative editing—and managing user roles accordingly. Users can assign roles such as viewer, editor, or owner, each with varying levels of permissions, allowing for flexible control over project access and editing capabilities.
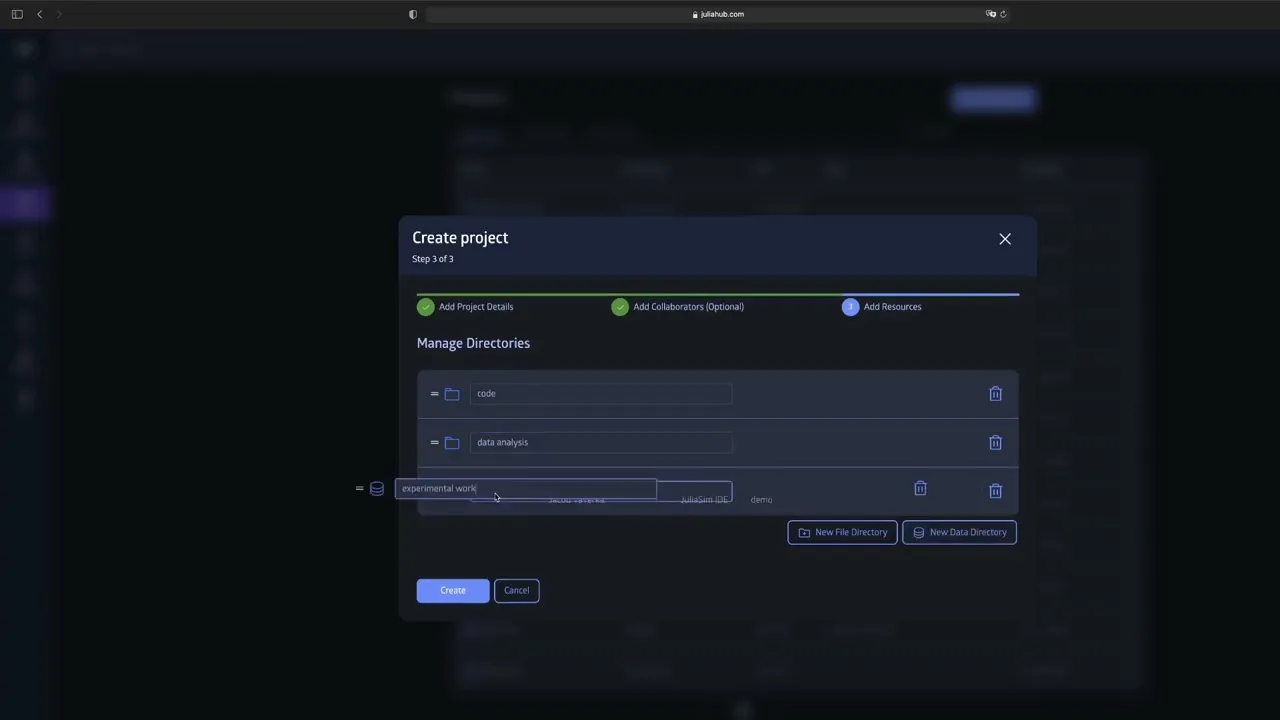
After setting up the project and permissions, the video explains how to add directories and resources, likening the directory structure to GitHub repositories. It demonstrates how to create subdirectories and files directly within the platform or through the connected IDE. Version control is also introduced through committing changes with descriptive messages, ensuring proper tracking of edits and updates.
The project dashboard is showcased as a central hub for managing projects. From here, users can view project contents, edit metadata, archive projects, mark them as complete, or reset and publish changes. Archiving a project removes it from the active dashboard but keeps it accessible in a separate archived section, with the option to restore it later. The video highlights the ease of managing projects, sharing, downloading, and renaming them, emphasizing the platform’s intuitive design and GitHub-like functionality. Overall, the tutorial offers a clear and practical guide to efficiently managing projects and collaboration within this environment.
Highlights
🆕 How to create a new project with a name, description, and tags for easy identification.
🛠️ Choosing a default application environment and workflow (exclusive vs. collaborative editing).
🔒 Assigning user roles with different permission levels: viewer, editor, or owner.
📂 Managing directories and resources similar to GitHub repositories.
💻 Using an integrated IDE (like Julia ID) to create, edit, and commit files directly.
📊 Project dashboard functionalities: view contents, edit metadata, archive, complete, and reset projects.
♻️ Archiving projects for temporary removal with an easy restore option and marking projects as complete.
Key Insights
🏗️ Project Setup Structured for Clarity and Collaboration: The step-by-step creation process—adding names, tags, descriptions, and default applications—ensures that projects are easily identifiable and accessible by team members. This organization facilitates collaboration and efficient project management.
🔄 Workflow Selection Impacts Collaboration and Control: Choosing between exclusive and collaborative editing workflows allows teams to tailor the project environment to their needs. Exclusive workflows restrict editing to select users, while collaborative workflows enable multiple users to work simultaneously, enhancing teamwork but requiring careful permissions management.
🔐 Granular Permission Management Enhances Security and Flexibility: Assigning roles such as viewer, editor, or owner with distinct permission levels allows project owners to maintain control over who can view, edit, or manage the project. This hierarchy helps prevent unauthorized changes while promoting transparency and accountability.
🗃️ Directory and Resource Management Mirrors Familiar GitHub Practices: By structuring projects with directories and subdirectories, the platform leverages familiar concepts from GitHub, lowering the learning curve for developers and facilitating organized data and code storage. This also streamlines navigation and resource allocation within projects.
💾 Integrated Version Control Boosts Productivity and Accountability: The ability to commit changes directly from the IDE with descriptive messages integrates version control seamlessly into the workflow. This practice not only helps track progress and changes but also supports rollback and auditing, which are critical for collaborative development environments.
🏢 Project Dashboard Centralizes Management Tasks: The dashboard acts as the control center, enabling users to manage project status, edit metadata, archive, publish, and reset projects. This centralization simplifies project oversight, reduces administrative overhead, and improves user experience by consolidating key functions in one place.
🔄 Archiving and Completion Features Support Project Lifecycle Management: The option to archive projects removes them from the active workspace but preserves their data for future restoration, offering flexibility in project lifecycle management. Marking projects as complete moves them to a finished section, helping teams track progress and maintain an organized project portfolio.
This video tutorial effectively demonstrates a user-friendly, GitHub-inspired project management system that supports flexible workflows, detailed permission control, and integrated development tools, all designed to enhance team collaboration and productivity.






